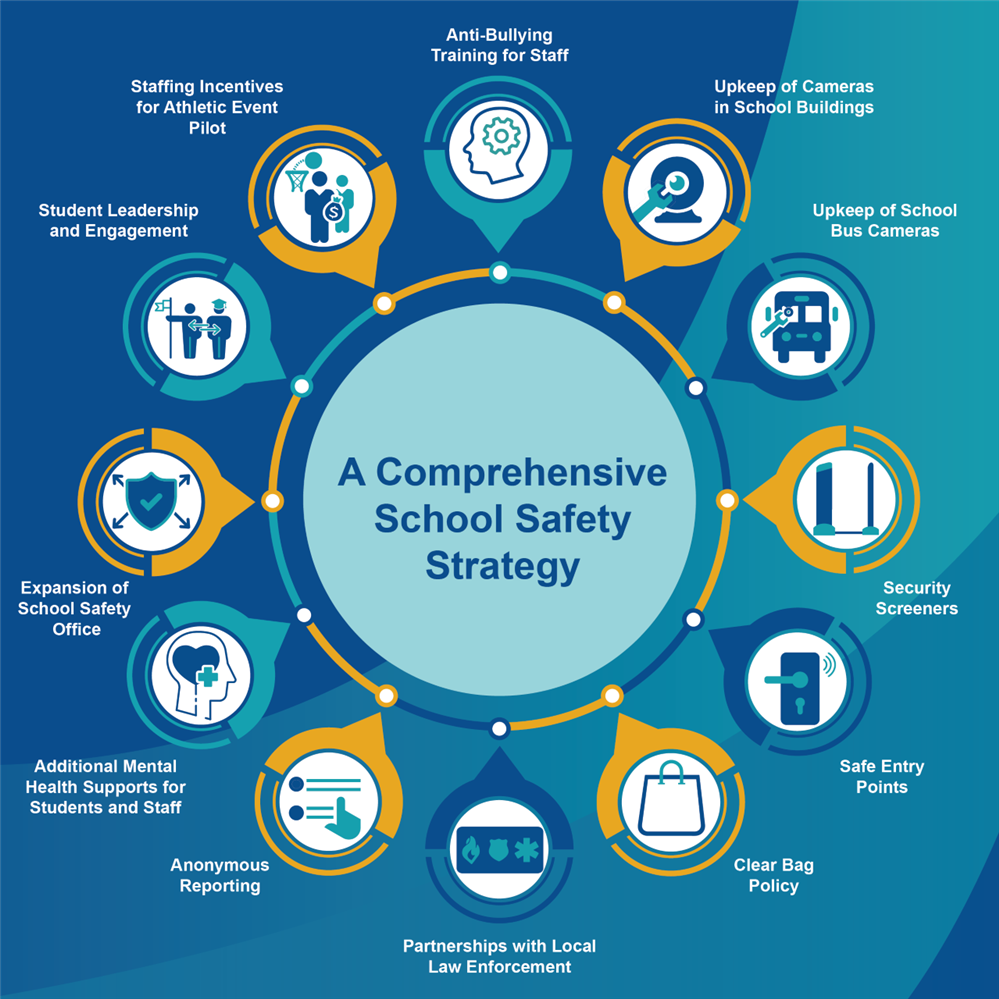
The Foundation of Safe School Transportation Policy
Introduction
School
transportation policies form the backbone of a safe and efficient student
transit system. A well-structured policy is not only about ensuring students
arrive on time but also about creating an environment that prioritizes safety
and accountability. Effective transport policies reduce risks, improve parent
confidence, and contribute to a school's reputation as a safe institution for
children.
Core Elements of a
School Transport Policy
At its core, a
school transport policy should address three critical areas: vehicle safety,
driver competence, and student behavior. Schools should ensure all vehicles
undergo regular inspections and comply with government-mandated safety
standards. Details such as functional seat belts, emergency exits, and proper
maintenance checks should be non-negotiable.
Driver training is
equally crucial. Drivers should be certified professionals, undergo background
checks, and attend periodic refresher courses. Schools can go a step further by
organizing defensive driving workshops and first aid training, preparing drivers
to respond effectively in emergencies.
Student behavior
policies are another essential component. Establishing a code of conduct for
students ensures discipline during transit. Simple rules like remaining seated,
no shouting, and refraining from distracting the driver go a long way in
preventing accidents.
Driver Training and
Supervision
Driver competence
directly influences safety. Schools must implement stringent hiring processes,
including comprehensive vetting of driver credentials. Periodic evaluations and
training help maintain high standards. Supervisors should conduct surprise inspections
to ensure compliance with policies.
Beyond training,
fostering a sense of accountability is key. Installing GPS systems in buses
ensures real-time monitoring, and cameras can provide additional oversight.
These measures not only boost safety but also help resolve disputes
efficiently.
Student Conduct and
Supervision
Students’ behavior
on buses is a reflection of the school’s culture. Clear guidelines must be
communicated to students and parents, ensuring everyone understands the rules.
Designating bus monitors or aides can provide additional supervision. These
individuals can mediate disputes, ensure compliance with safety norms, and
report incidents to school authorities.
Engaging parents is
another critical strategy. Schools should organize workshops to explain
transportation policies, highlight the importance of adhering to them, and
encourage parents to reinforce these rules at home.
Case Example
The XYZ School
District implemented a comprehensive transport policy that emphasized regular
vehicle inspections, driver training, and strict student conduct rules. Over a
year, bus-related incidents, including minor disputes and disciplinary issues,
decreased by 40%. Parents expressed increased satisfaction and trust in the
school’s commitment to student safety.